반응형
Notice
Recent Posts
Recent Comments
Link
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
| 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 |
| 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
Tags
- centrifugal pump working principle
- health benefits of chives
- pump operation methods
- honey for better circulation
- ginger tea to raise body temperature
- api standard pumps
- natural remedies for cold hands and feet
- tbe report preparation guide
- pump applications and case studies
- managing vendor print schedule in engineering projects
- design progress management
- pump classification criteria
- types of industrial pumps
- features of different pump types
- vendor data requirement (vdr) review
- key steps in vendor selection for epc contractors
- plant operation and maintenance documentation
- piping design standards
- piping stress analysis
- difference between dynamic pumps and positive displacement pumps
- how to prevent colds with food
- equipment data sheet and technical specifications
- foods that boost body temperature
- pump design standards
- walnuts for winter health
- warm-up foods for winter
- definition and types of pumps
- environmentally friendly power plant
- radish for improving circulation
- healthy winter snacks for warmth
Archives
- Today
- Total
Safety Balance
Piping Stress Analysis Methods and Applications 본문
반응형
▣ Classification of Piping System Stresses
- Primary Stress
- Stress induced by forces and moments applied internally and externally to the piping system, including bending stress from internal pressure, self-weight, wind, and other factors, as well as torsional stress.
- The safety of primary stress is evaluated by comparing it with the allowable stress of the piping material.
- Secondary Stress
- Stress caused by thermal expansion due to the temperature of the fluid flowing through the pipeline. Even if this stress exceeds the yield strength of the material, it can enter a safe stress range due to stress relaxation.
- Unlike primary stress, secondary stress is not compared directly with the allowable stress but rather with the allowable stress range to determine safety.
- Allowable Stress
- The stress level that a material can safely withstand under various temperature conditions concerning primary stress.
- These values are provided in the ANSI Code.
▣ Types of Stresses
- SI: Longitudinal Stress
- Sc: Circumferential Stress
- Sr: Radial Stress
- Ss: Shear or Torsional Stress

▣ Static Stress Analysis
- Sustained Load: Includes dead weight and internal pressure.
- Occasional Load: Includes wind load and seismic load.
- Support: Analysis of self-weight, hydrodynamic pressure, and reaction forces.
- Evaluation of Impact on Connected Equipment Due to Forces & Moments:
- Includes rotating machinery such as pumps, compressors, turbines, and air fin coolers.
- Evaluates nozzle load stress for vessel nozzles (cylindrical, spherical) and heaters.
- Stiffness Ring Design for Vacuum Lines.
- Underground Stress Analysis: Includes thermal and earth pressure design.
- Branch Reinforced Pad Design.

▣ Dynamic Stress Analysis
- Safety Valve Thrust Calculation.
- Vibration: Includes considerations for reciprocating compressors and two-phase flow.
- Seismic Analysis: Includes static method and response spectrum method.
- Surge Analysis: Involves determining energy absorption devices due to sudden pressure rises in long-distance high-speed fluid pipelines, caused by rapid valve switching or power outages.
▣ Flexibility Analysis of Piping
- Flexibility analysis involves reviewing whether the piping between fixed points has adequate flexibility to accommodate thermal expansion, ensuring that pipe supports are designed to withstand sustained and occasional loads.
- The flexibility analysis is performed to ensure the proper layout of the piping, and it typically does not require a special calculation procedure or the creation of a calculation report as part of the piping stress analysis documentation.
- It is not necessary to perform flexibility analysis for every piping system.
Cases Where Analysis is Not Required (ASME B31.1):
- The installed piping system is identical to a system with proven usage or is a replacement for such a system.
- The installed piping system is judged to be adequate when compared to a previously stress-analyzed system.
- The installed piping system has a constant diameter, no restraints between two anchors, and the total number of operating cycles is 7,000 or less, satisfying specific equations.

▣ Piping Stress Analysis Codes
- API675: Positive Displacement Pumps Controlled Volume
- API-618: Reciprocating Compressors For General Refinery Services
- NEMA SM23: Steam Turbine For Mechanical Drive Service
- API-560: Fired Heaters For General Refinery Services
- API-610: Centrifugal Pumps For General Refinery Service
- API-611: General-Purpose Steam Turbines For Refinery Service
- API-612: Special-Purpose Steam Turbine For Refinery Service
- API-617: Centrifugal Compressors For General Refinery Service
- API-661: Air-Cooled Heat Exchangers For General Refinery Service
- API-650: Welded Steel Tanks for Oil Storage
- API-1102: Liquid Petroleum Pipelines Crossing Railroads and Highways
- ANSI A58.1: Minimum Design Loads For Buildings and Other Structures
- ANSI B31.3: Chemical Plant and Petroleum Refinery Piping
▣ Stress Analysis Report
- After performing stress analysis, document the results and retain them for reference.
- Includes applied codes, computer programs, and general information.
- Assumptions applied in the design.
- Hold Item Lists.
- Isometric Drawings used for piping stress analysis (including input data).
- Computer input data (design conditions, material properties).
- Basis for thermal expansion displacement calculations for equipment.
- Review of nozzle loads based on load combinations.
- Load Summary Sheets for anchors and supports based on load combinations.
- Computer-generated results, etc.
▣ Review Items After Analysis of Self-Weight, Occasional Load, and Thermal Expansion
- Is the sag of the piping due to self-weight within acceptable limits?
- Are the loads on equipment nozzles within allowable limits?
- Is the maximum stress within the allowable stress?
- Are excessive loads generated on the designed anchors?
- Is there an upward load (Up-Lift Load) due to the load?
- Does the thermal expansion displacement cause interference with nearby piping?
- Are there lower points than the drain point due to thermal expansion?
- Are the analysis results within allowable limits for each operating mode?
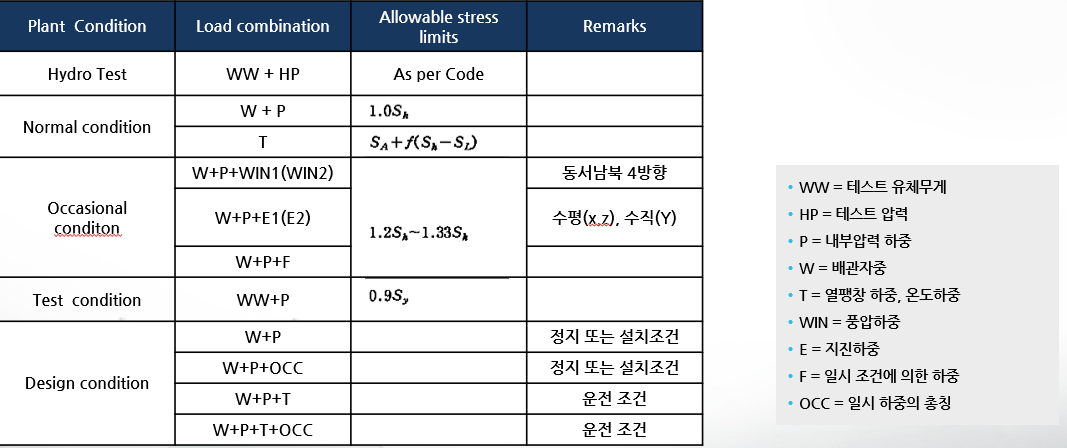
▣ Load Combinations and Allowable Stress
- Design Condition:
- Considerations include the piping's self-weight (including the weight of the fluid, insulation, concentrated loads such as valves), design pressure, seismic load, etc.
- Normal Operating Condition During System Operation:
- Includes piping self-weight, internal pressure, thermal expansion load, and abnormal conditions that may occur during operation.
- Includes dynamic loads, internal pressure, and thermal expansion loads.
- Test Condition:
- Testing considerations.
▣ Load Combinations (ASME B31.1)
▣ Coordination with Other Disciplines
DisciplineMain Coordination Tasks
| Structural | - Transfer of dead load and anchor load, thermal load transmission - Verification of seismic and wind load design criteria |
| Civil | - Transfer of foundation load for independent supports - Receipt of seismic and wind load design criteria |
| Equipment | - Transfer of nozzle load (Force & Moment) results - For general vessel nozzles, verification of analysis results by equipment design personnel - For high-temperature, high-pressure vessels, verification by equipment design personnel or manufacturer |
| Mechanical | - Request for verification of rotating equipment nozzle loads - Confirmation of nozzle integrity by mechanical personnel or manufacturer |
반응형
'Technical' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Characteristics of Mechanical Design in Plant Engineering (0) | 2024.08.21 |
|---|---|
| Plant Construction Business and Mechanical Design (0) | 2024.08.21 |
| Overview and Purpose of Piping Stress Analysis (0) | 2024.08.20 |
| "Standards Applied in Piping Design" (0) | 2024.08.06 |
| Piping Stress Analysis (0) | 2024.08.06 |




